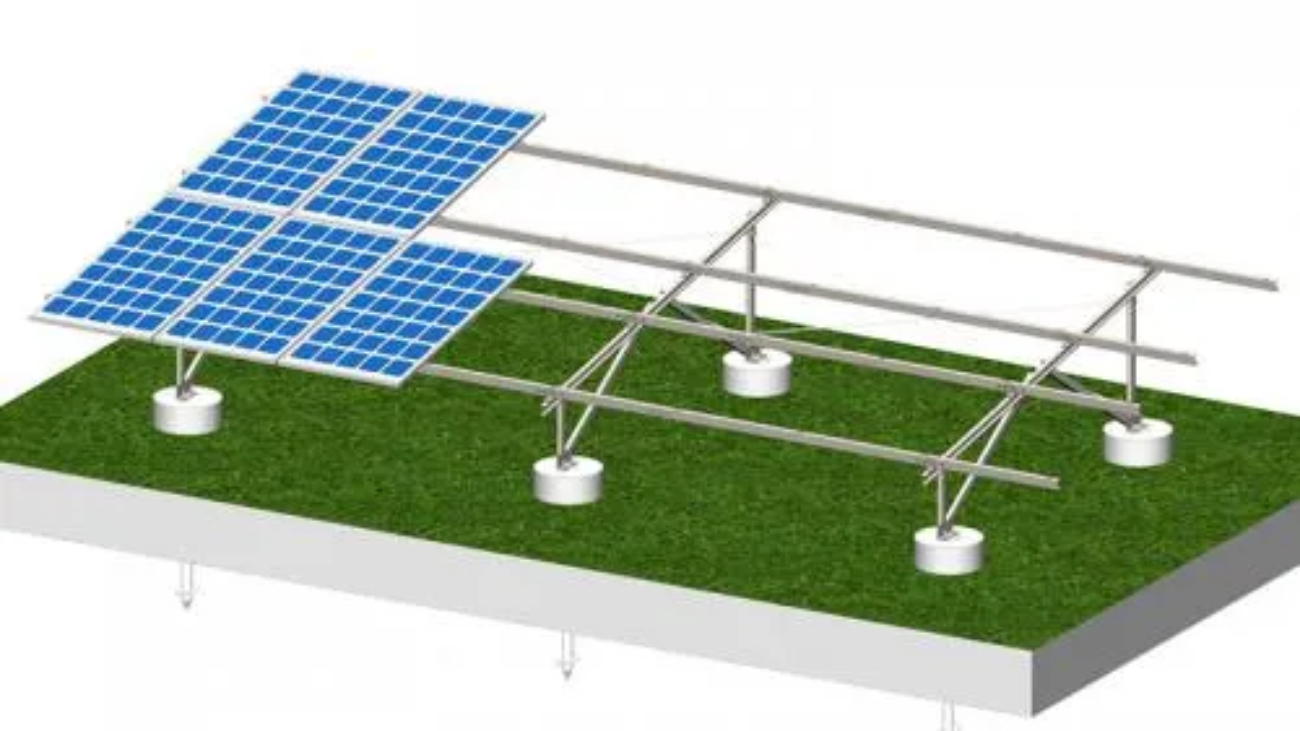
I. Introduction to Ground Mounting Structures

In Structura Metal a ground mounted setup refers to a solar panel system that is installed directly into the ground rather than on a roof. Ground installations have become increasingly popular for both residential and commercial solar projects. There are several key benefits that the ground mounts provides over rooftop solar systems:
- More flexibility in panel placement.
- Increased energy production.
- Easier maintenance.
- Avoid roof obstacles and structural issues.
At Structura Metal Ground Mounted Solar offers much more flexibility in where you can place panels to optimize sun exposure. With a rooftop system, you are also having limitations for the shape and directions of the areas available. Ground mounts allow placement in the wide open spaces without blocking the sunlight.
In addition, we also having the open airflow beneath ground mounted panels helps to keep the temperatures lower. This allows for more efficient energy conversion and increased energy production compared to rooftop systems. Studies show ground mounted solar can produce 10-45% more energy than the fixed rooftop setups.
| Benefits | Ground Mounted Solar | Rooftop Solar |
| Flexible placement | ✅ | ❌ |
| Increased production | ✅ | ❌ |
| Lower temperatures | ✅ | ❌ |
| Easy maintenance | ✅ | ❌ |
Furthermore, a ground mounting system avoids any roof structural issues or the obstacles like vents, chimneys etc. And since panels are more accessible on the ground, overall maintenance is simpler without working from heights or ladders.
With all these advantages, it’s no wonder ground mounting structures are becoming the preferred mounting solution for many solar projects. Keep reading to learn more about the different types of ground mounted options available.
II. Strengths of Ground Mounted Setups
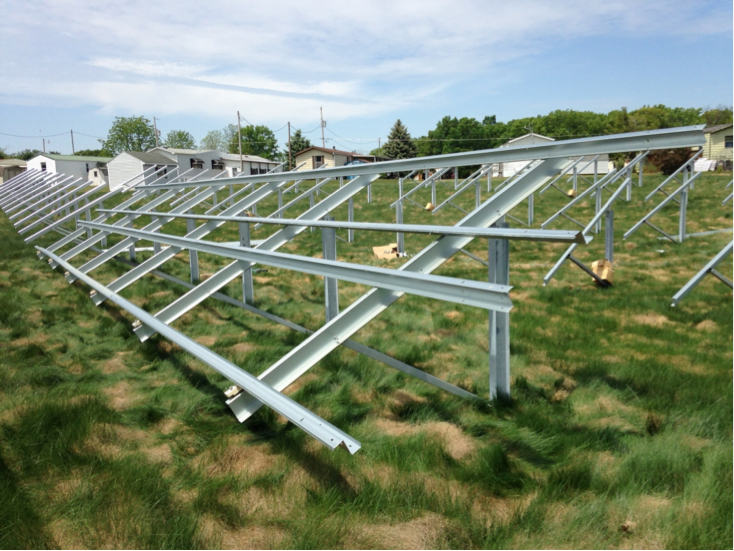

Installing a solar panel system on the ground rather than the roof offers some unique advantages. Here are the main strengths of ground mounted setups:
- Orientation and Angle Flexibility – With ground mounts, we are having the panels that can be positioned at the optimal angle and directions to maximize sunlight exposure. You are not limited by the shape or direction of the areas on your roof.
- Higher Energy Production – The open airflow underneath helps keep temperatures lower. This allows ground mounted panels to convert sunlight to energy more efficiently, generating 10-45% more power.
- Easy Maintenance – Accessing rooftop solar panels typically requires climbing ladders or using special equipment. Ground mounts are closer to the ground, making regular inspection and cleaning much simpler.
- No Rooftop Restrictions – Rooftop solar projects may be limited by structural issues, vents/chimneys, or lack of space. Ground mounts avoid all the rooftop restrictions.
- Land Restrictions – While rare, some neighbourhoods have rules against installing visible solar panels. Ground mounts may need to be hidden behind the fences or vegetation.
III. Weaknesses of Ground Mounts
While ground mounted solar offers significant advantages, there are some potential downsides to consider as well:
- Higher Installation Cost – In general, a ground mounting system has a higher upfront price tag than an equal sized rooftop system. The racking and foundation materials, digging/trenching, and labour make it more expenive.
- Land Restrictions – Although rare, some neighbourhoods prohibit visible renewable energy systems or restrict their placement. Ground mounts may need creative vegetation or fencing.
- Safety Concerns – Since panels are accessible, a ground mounting structure poses a minor risk for kids or pets walking into them. Proper fencing helps mitigate this.
- Damage Risks – Rooftop solar is largely protected from incidental damage. However, ground mounted panels may be exposed to vehicles, animals, weather events, vandalism etc.
- Aesthetic Impact – Low profile ground mounts usually blend into landscapes well. But some systems stand out and homeowners may prefer to keep their yard/lawn view unchanged.
| Weakness | Risk Level | How to Mitigate |
| Cost | High | Get multiple installer bids to reduce price |
| Land rules | Low | Petition for renewable energy exceptions |
| Safety | Low | Add fencing around solar system |
| Damage | Low | Add protective barriers as needed |
| Aesthetics | Low | Use vegetation to hide/blend system |
IV. Types of Ground Installations
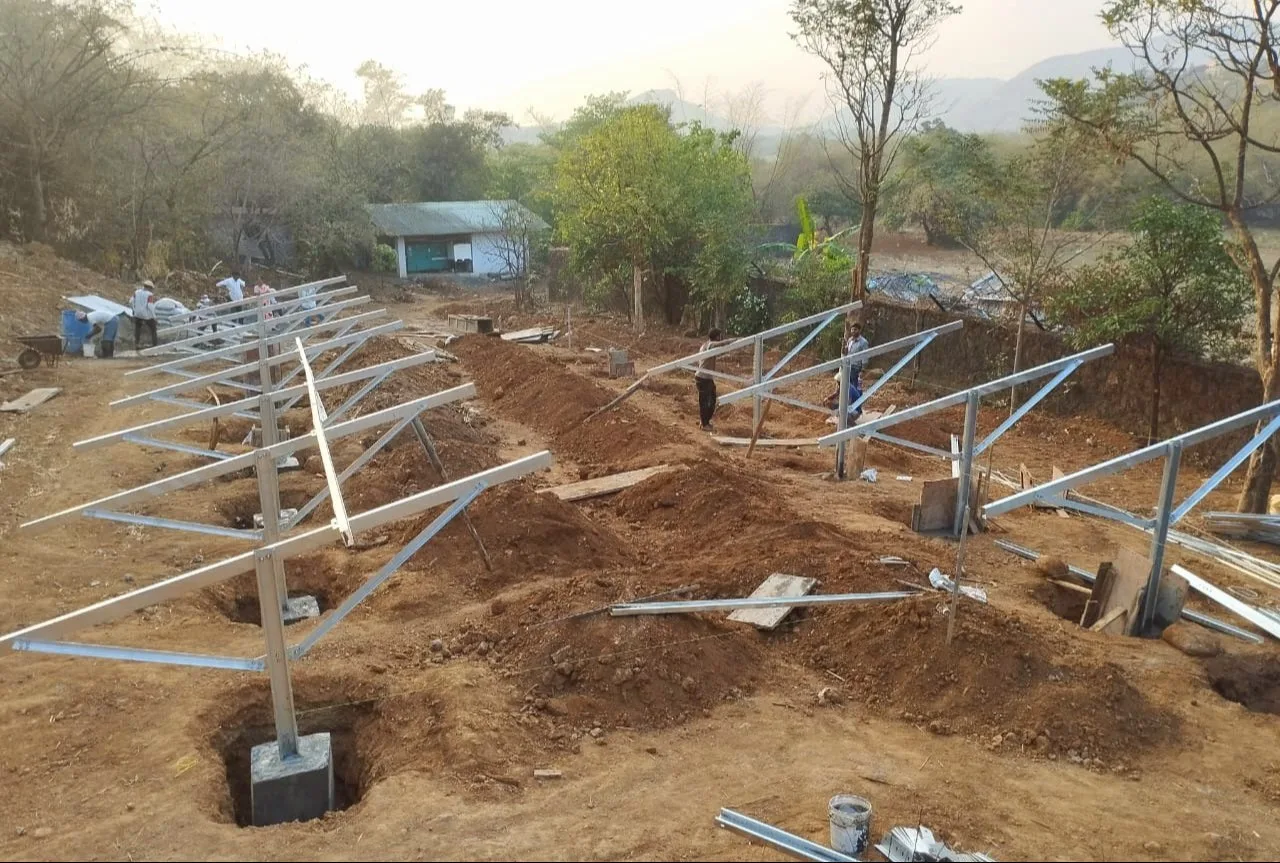

If you decide to install the ground mounted solar system, you have several options when it comes to the specific type of mounting structure. The three main types of ground installations are:
- Traditional ground-mount
- Tracking systems
- Carports and canopies
Traditional ground-mount systems use to anchors and robust structural racking to fix panels in an optimal position. This is the most common type of ground mounted system.
Tracking Systems go by step further by using automated hardware to move panels and follow the sun’s path during the day. This further maximizes energy production but has a higher cost. Single-axis trackers shift panels east-west or north-south to capture more sunlight. More advanced dual-axis trackers can shift in multiple directions to keep panels perpendicular to the sun’s rays.
Carports and Canopies utilize very large Ground Mounted Structures as coverage for vehicles in parking lots or other uses. For example, a solar carport can provide shade for cars while generating clean power.
| System Type | Cost Level | Maintenance | Ideal For |
| Traditional | Low | Low | Most installs |
| Tracking | High | Medium | Large installs |
| Carports | High | Low | Commercial |
Determine the scale of your solar needs and budget to decide which type of ground installation makes the most sense. Tracking systems produce a good amount of extra energy but carry a cost premium over traditional fixed racking.
V. Traditional Ground-Mount Systems
The most common and cost-effective type of ground mounted solar setup is the traditional fixed racking system.
Traditional ground-mount systems work similarly to rooftop mounts. Panels get attached with the strong metal frame and angled to optimize sun exposure. Instead of being installed on singles though, the racking frame mounts directly into the ground with the pier or anchor supports.
Benefits of traditional fixed ground mounting:
- Low Cost – Traditional mounts have the lowest hardware and installation the costs per watt over other ground systems. This makes it affordable for most homeowners.
- Easy to Install – For most residential sites, traditional fixed mounts can be fully installed in 1-3 days with a small crew minimizing labour expenses.
- Low Maintenance – With no moving parts or motors, traditional systems require very little ongoing maintenance besides occasional panel cleaning.
- Expandable – Additional panels can be easily added later on to increase your system size. The fixed mounting structure is designed for modular expansions.
The simplicity, affordability, and reliability of fixed position ground mounting structures make them a top choice. The only downside is they lack the sun tracking advantage of more complex systems. But the better return on investment keeps traditional mounts popular for residential installs.
VI. Tracking Systems
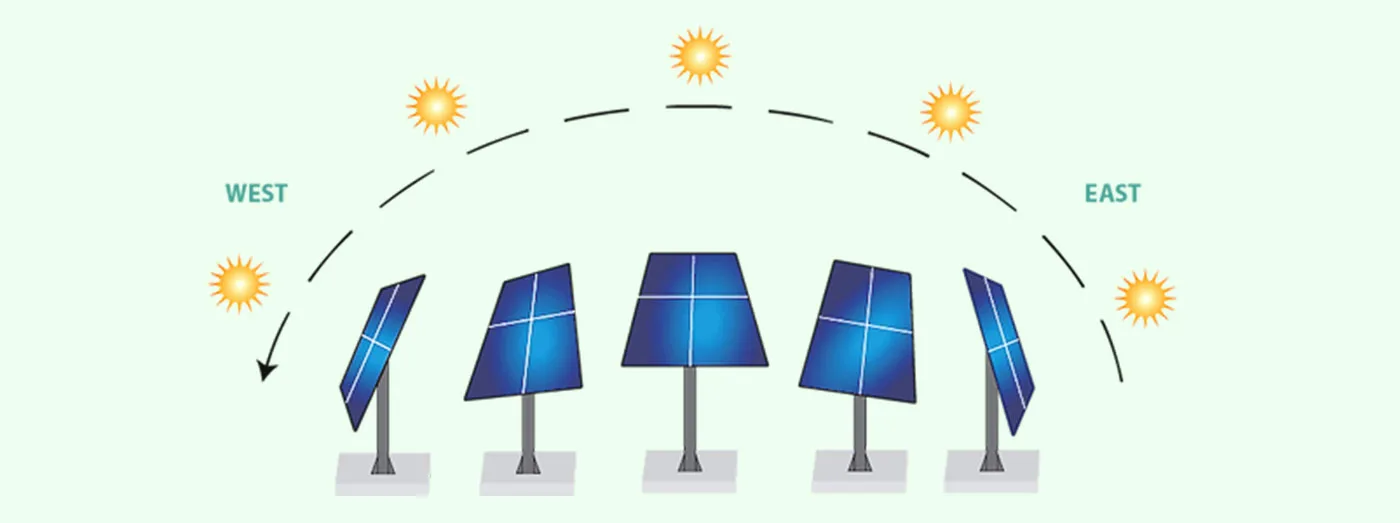
Tracking systems take ground mounted solar technology to the next level for maximum sunlight capture and energy production. These systems utilize motors, sensors, and controlers to automatically move solar panels over the course of a day. By keeping panels aligned perpendicular to the sun’s rays, they generate up to 45% more power annually.
There are two main types of solar trackers used with ground mounts:
- Single-Axis Trackers: Rotate panels along one axis to follow the sun east to west.
- Dual-Axis Trackers: Rotate panels along two axes enabling full 360 degree range of motion to precisely face the sun all day.
Benefits provided by tracker ground mounting:
- Greatly increased energy yield per panel
- Optimized spacing between rows of panels
- Better performance in winter months
- Reduced shade impact
The main disadvantages of using solar trackers are higher hardware costs, more complex installation, and increased maintenance requirements. Trackers utilizes motors, controllers, wiring, and gears that may eventually need replacement. Proper installation is also key for reliability.
Overall, the pros of solar tracking capabilities often outweigh the extra costs for larger commercial ground mounting projects. The significantly higher energy production provides better and faster return on investment. But trackers may be excessive for smaller residential ground installs where fixed mounts sufficient.
VII. Carports and Canopies

Carports and canopies utilize very large ground mounting structures that serve dual purposes. They provide shade or shelter, while also hosting solar panels to generate significant amounts of the electricity.
The most iconic example is the solar carport. As the name suggests, solar panels get installed on the roof structure of a carport. This keeps vehicles underneath shaded from the elements, while the panels above soak up the sunlight. The collected energy can then power buildings, electric vehicle charging stations, or get fed back into the grid.
Solar canopies function similarly, by mounting panels on top of a steel structure designed specifically for shade. You often see these utilized in parks, schools, and playgrounds to produce renewable power in addition to shielding what’s underneath.
Benefits of solar carports and canopies:
- Large open spaces for mounting many panels.
- Dual purpose installations (power + shelter).
- High visibility demonstrations of clean energy.
The main barriers to larger carport or canopy projects have traditionally been the high upfront design and material costs. However, as solar panel prices continue to fall, these types of installations are becoming more financially viable. And they serve as impactful sustainability symbols for schools, commercial centres, and other public spaces.
VIII. Cost of Ground Mounted Systems
Installing a ground mounted solar array comes at a higher initial price tag than rooftop solar. There are several cost factors that contribute to this:
- Structural Materials – Industral grade aluminium and galvanized steel is used to assemble the racking, poles, and foundations. These materials are more heavy duty than typical rooftop mounts.
- Excavation And Equipment – Digging holes for foundations, trenching electrical wires, renting heavy machinery, and transporting materials add to project costs.
- Labour – Ground mount installations take longer and often require crane equipment to position modules. More man hours equals more labour expense.
However, against these higher upfront costs are the long term savings:
- Increased Energy Production – The optimal positioning and solar tracking capabilities lead to significantly more clean energy generated.
- Accelerated depreciation further reduces tax burden.
Over time, the extra energy and financial incentives make ground mounted systems pay for themselves more rapidly compared to equivalently sized rooftop installs. And protection from weather/debris means savings on roof repairs.
IX. Maintenance of Ground Mounted Solar

A key advantage of ground mounted solar is that regular maintenance is easier than rooftop systems. Accessing panels on the ground avoids the need for ladders or technical rope training. Basic upkeep best practices include:
Inspections
- Inspect all wiring, mounts, gear boxes for damage quarterly. Repair any loose connections or corrosion.
- Check panel glass for cracks/chips annually which could allow moisture damage.
Cleaning
- Clear any accumulated leaves/debris around the mounting structure.
- Wash panels with soft brushes and water at least twice per year for maximum solar absorption.
Vegetation trimming
- Trim any nearby plants/branches that may overhang and put panels in shade. Sunlight occlusion severely reduces output.
Snow Removal
- Use non-abrasive plastic shovels to clear heavy snow off panels after storms.
Tracking & Monitoring
- Ensure tracker motors function properly in all seasons.
- Monitor production output levels monthly to catch any decreased yields from common culprits like dirty panels, tracking miss collaboration, or wiring issues.
Following this basic preventative maintenance checklist for your ground mounted system improves reliability, extends equipment lifespan, and maximizes solar energy production year after year.
X. Conclusion
Installing solar panels on the ground rather than roofing provides unique advantages. Ground mounted solar gives you flexibility on placement for optimum sunlight exposure for leading to significantly higher energy generation. The ability to incorporte tracking systems takes this productive potential even further.
As solar panel and storage prices continue falling, renewable energy adoption will only accelerate further. Both rooftop and ground mounted solutions each have ideal applications depending on the site constraints and power demands. Consult with qualified solar professionals to map out the best clean energy generation plan tailored for your home or business.

