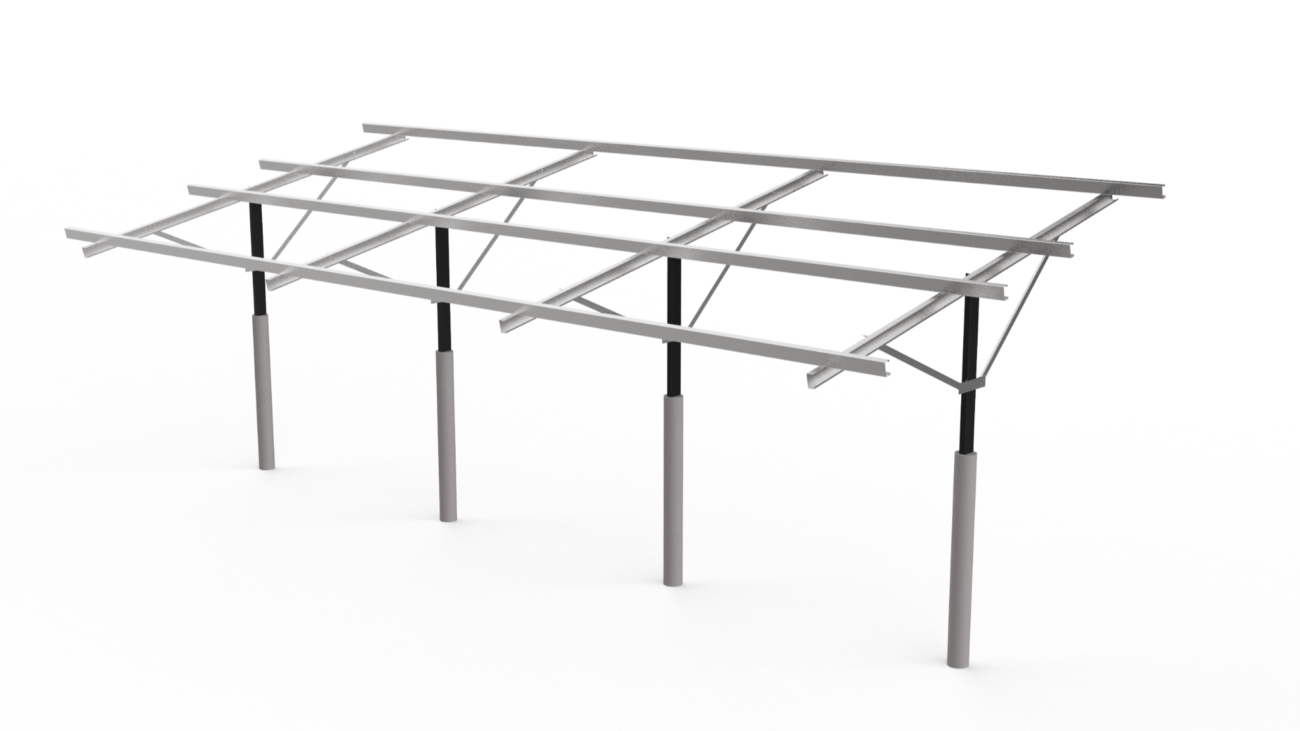
I. Selecting Solar Mounting Structures
Carefully selecting solar mounting structures is crucial in maintaining solar panel performance and system longevity. This process involves geological surveys, soil condition analysis, fixed tilt and tracker design considerations, and recommendations from advanced modelling tools.
Foundation Requirements
Our geological surveys must be performed to determine the optimal type of foundation for the solar mounting system, assessing:
| Factors | Recommendations |
| Soil acidity | Apply protective coating if needed |
| N values | Indicative of soil strength |
| Groundwater | Prevent corrosion |
| Soil conditions | Detailed analysis |
Plant Design Considerations
The mounting structures must account for the planned plant design:
- Fixed tilt: Angled at optimal degree for site location
- Trackers: Follow sun throughout the day, best suited for flat sites
Analyse topography to account for complex terrain:
- Foundation pile lengths
- Model shadowing
- Streamline parts and installation
Automated Recommendations
Leverage advanced modelling software like Rated Power to automate:
- Plant layout optimization
- Component selection for environmental conditions
- Cost, performance and profitability projections
These tools provide data-driven recommendations to optimize mounting structure selection based on the project goals and constraints.
Their projections help determine required:
- Pole diameter and depth
- Fastenings rated for extreme weather
- Reinforcements to prevent collapse
Carefully weighing these considerations enables selection of cost-effective, durable solar mounting systems able to withstand decades of operation.
II. Mounting Structure Types
The soil conditions and operational environment dictate the optimal mounting structure. Main options:
Ballast Mounts

- Pre-cast concrete block
- Rest on compacted soil
- Residential rooftop installations
- Avoid need to drill/excavate
Helical Piles
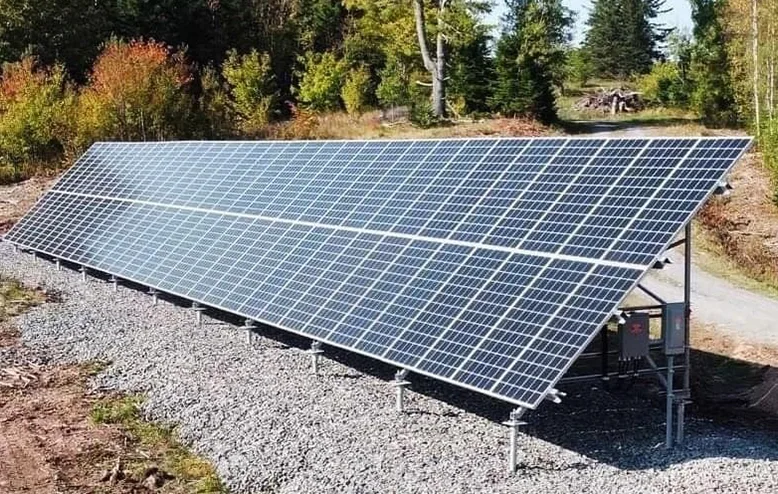

- Driven into soil conditions
- Withstand uplift forces
- Resist expansion and strong winds
- Provide load-bearing capacity
Pole Mounts
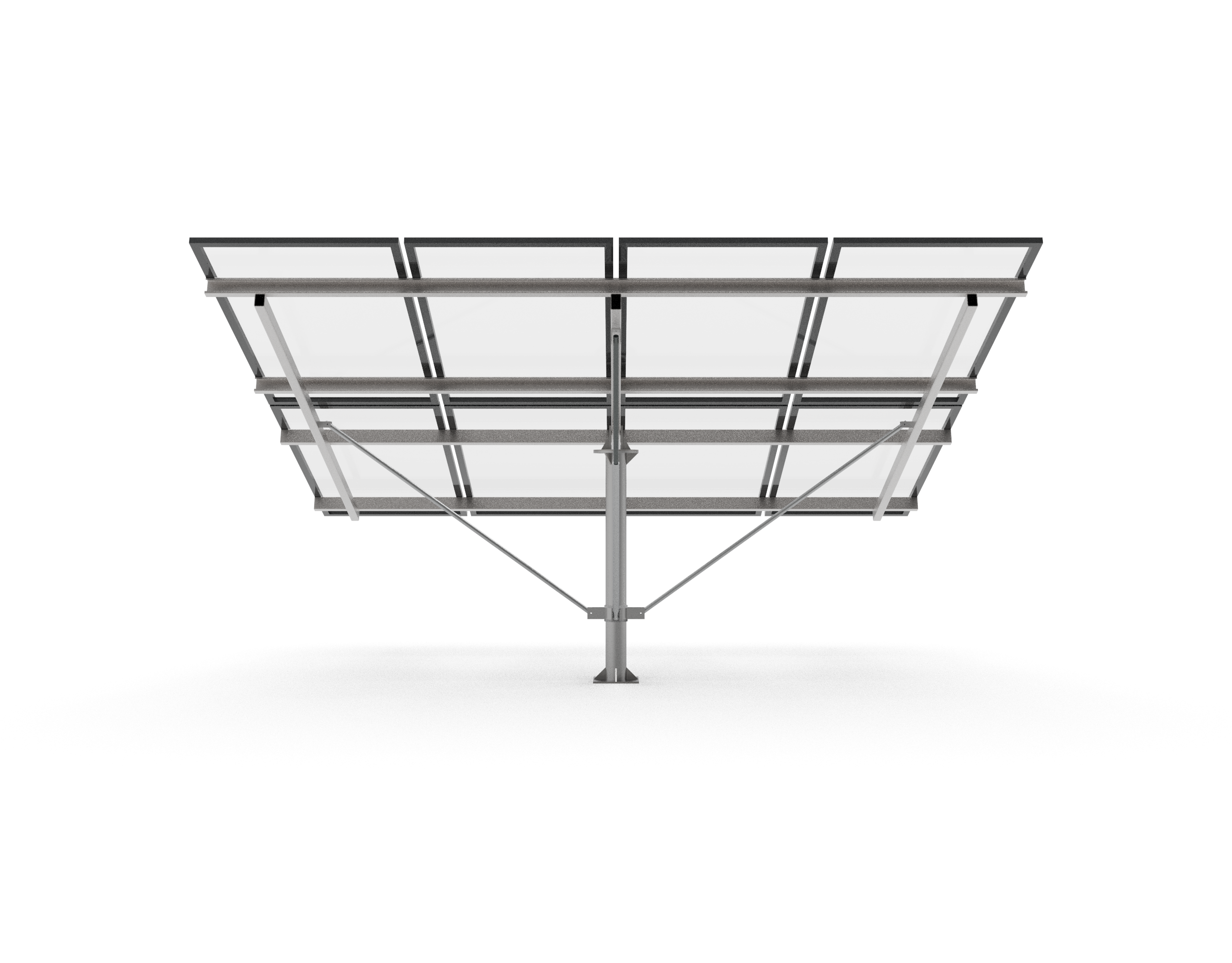

- Steel poles with concrete anchors
- Simpler than ballast mounts
- Multi-pole systems
- Single row of panels
- Ease large project adjustments
Ground Screws
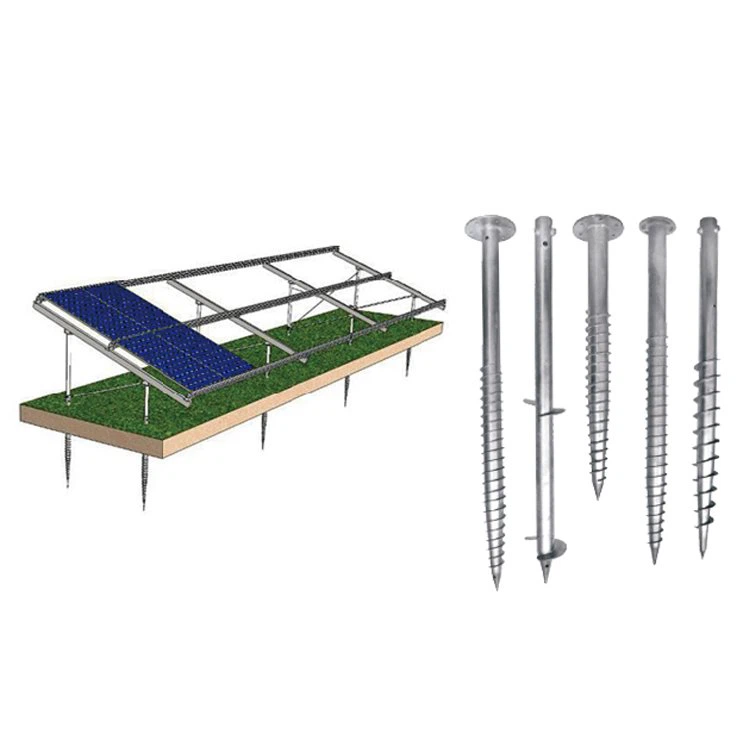

- Soil conditions:
- Compacted
- Heavy clay
- Rocky surface
- Minimal earthwork and engineering
| Factor | Considerations |
| Steep terrain | Screws have limited gradient suitability |
| Granular soils | Provide less stability |
Concrete Foundations
- Ideal for:
- Brownfield sites
- Capped landfills
- Wetland sites
- Minimally invasive mounting
Careful analysis of the site geological surveys and planned solar farm size determines optimal structure types.
III. Structure Installation
Once the mounting structure type is selected, proper installation is key to ensuring solar farm performance and longevity.
Location Planning
- Survey site topology
- Mark locations for:
- Mounting structure base
- Foundation piles
Considerations:
- Access for construction equipment
- Optimizing spacing and tilt angles
- Minimizing shading
Foundation Installation
Method depends on structure type:
- Ballast
- Level ground
- Position blocks
- Bolt to frames
- Piles:
- Drive into ground
- Depth based on soil, loads
- Attach to structure
- Screws:
- Mechanically screw in
- Add torque as needed
- Concrete:
- Cast foundation
- Cure properly
- Attach racks
For small sites, hand tools can be used. Larger solar farms require:
- Excavation equipment
- Pile driving machinery
- Cement pouring
Other Considerations
- Schedule installs around rain to allow proper curing
- Check for shift/corrosion periodically
- Assess after extreme weather events
Proper base structure installation ensures the solar farm can withstand environmental conditions for the project lifetime.
IV. Failure Modes
Improperly designed or installed mounting structures can fail, causing solar farm damage or collapse.
Design Failures
Inadequate design is a common failure mode:
- Incorrect tilt angle
- Reduces energy generation
- Accelerates weathering
- Insufficient corrosion planning
- Shortens lifespan
- Risks collapse
- Not accounting for environmental conditions
- Wind, snow, rain loads
- Seismic factors
- Lightning strikes
Use advanced modelling tools during design to predict and address these factors.
Installation Failures
Faulty foundation installation causes most failures:
- Improper pile depth
- Loosens over time
- Insufficient anchor
- Inadequate curing
- Weakens concrete
- Cracks under load
- Poor leveling
- Twists structure
- Unbalances loads
Conduct pull-out testing after install to validate integrity.
Impact
- Panel damage from detached arrays
- Destabilized ground
- Risks landslides
- Further equipment damage
- Lost energy generation
- While repairs conducted
- If decommissioned
Preventing mounting structure failure is crucial for utility-scale solar farm optimization. Adequate design and installation is key.
V. Advanced Modelling
We specialized solar design software leverages advanced algorithms to streamline and optimize mounting structure selection.
Key Features
- 3D site modelling
- Analyse terrain
- Identify ideal layout
- Automated engineering
- Foundation sizing
- Pull-out calculations
- Structural analysis
- Machine learning
- Data from prior projects
- Improves recommendations
- Custom reporting
- Details selections
- Installation guidelines
Automated Deliverables
Extract key project outputs:
- Bill of materials
- Parts, quantities, costs
- Permit drawings
- Submit directly
- Installation plans
- Equipment needs
- Construction schedule
Continuously optimize as design evolves:
- Adjust for equipment purchases
- Update code compliance
- Reruns in seconds
Why automate?
- Eliminates error-prone manual work
- Provides data-backed recommendations
- Saves significant time and costs
- Enables design of high-performing mounting solution
Leveraging advanced tools ensures selection of ideal, cost-effective mounting systems for each unique solar site.
VI. Next Steps
Properly designing and implementing solar mounting structures is critical for project success. Key recommended next steps:
Detailed Site Analysis
Perform in-depth site surveys assessing:
- Soil conditions
- Composition
- Load capacities
- Topography
- Height variations
- Obstacles
- Accessibility
- Construction equipment
- Maintenance needs
This data informs ideal mounting structure planning.
Design Optimization
Leverage advanced algorithms to automate optimizing for:
- Energy generation projections
- Land usage efficiency
- LCOE minimization
- Custom objectives
These tools run iterative simulations to determine optimal:
- Tilt angles
- Foundation sizing
- Pole configuration
- Tracking capabilities
Streamlining mounting structure design enables maximized ROI.
Demo Request
See a live demo of data-driven mounting structure optimization in action:
- Custom 3D site modelling
- Foundation design
- Automated BOM generation
- Performance/cost projection
Understand capabilities before committing, to ensure solution adequacy for specific project needs.
Implementation Planning
With optimized mounting structure selection completed, detailed implementation planning is next:
- Permitting
- Grid interconnection
- Foundation and structure installation
- Panel mounting
- Inspection
Proper construction is vital for protecting long-term solar farm durability against extreme weather and maximizing energy generation.
We provide careful planning and leveraging modern solar design tools enables streamlined mounting structure implementations for productive, profitable solar projects.

