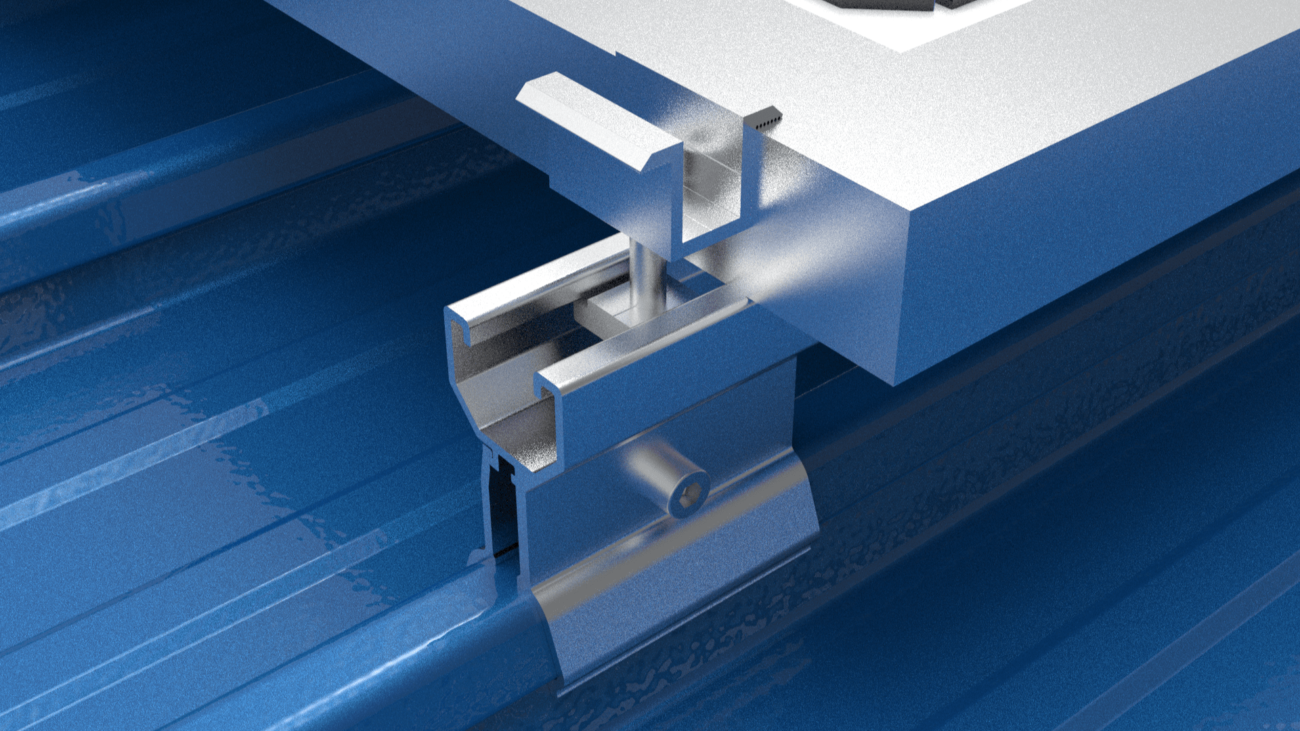
C Channel
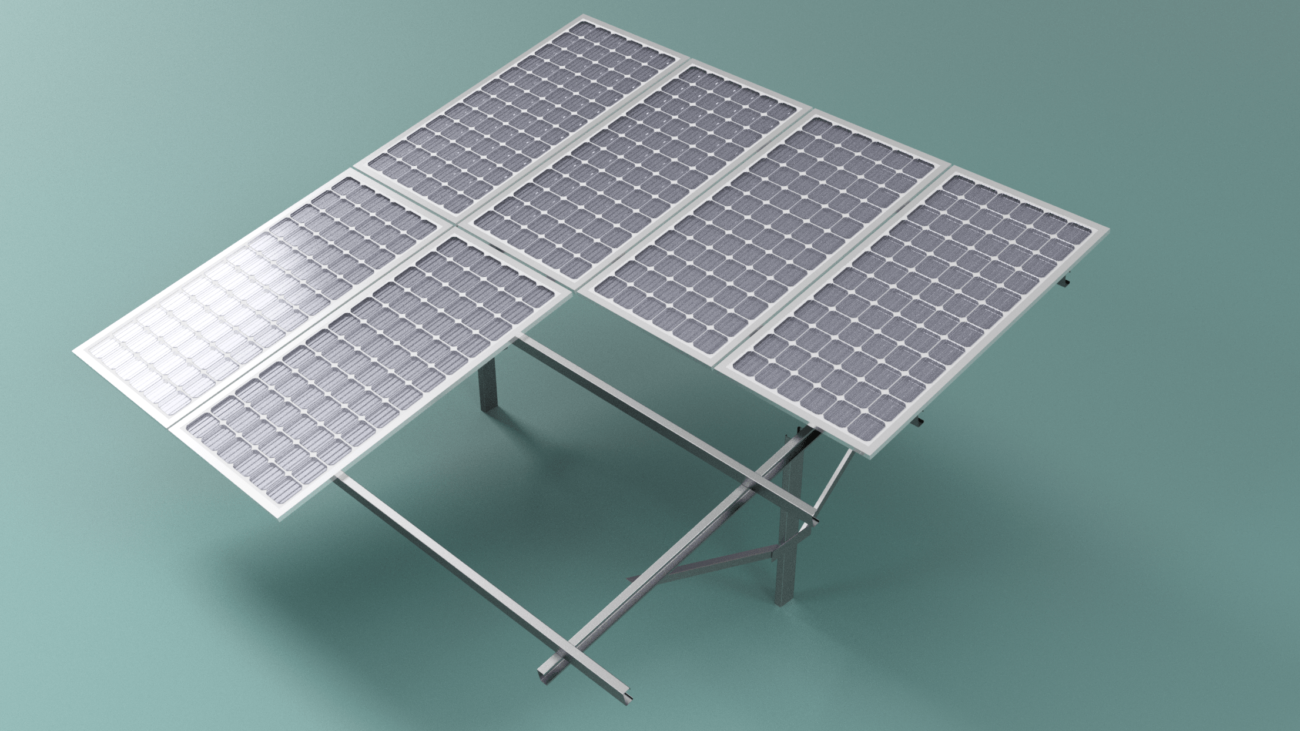
Solar Mounting System on Standing Seam Roofs
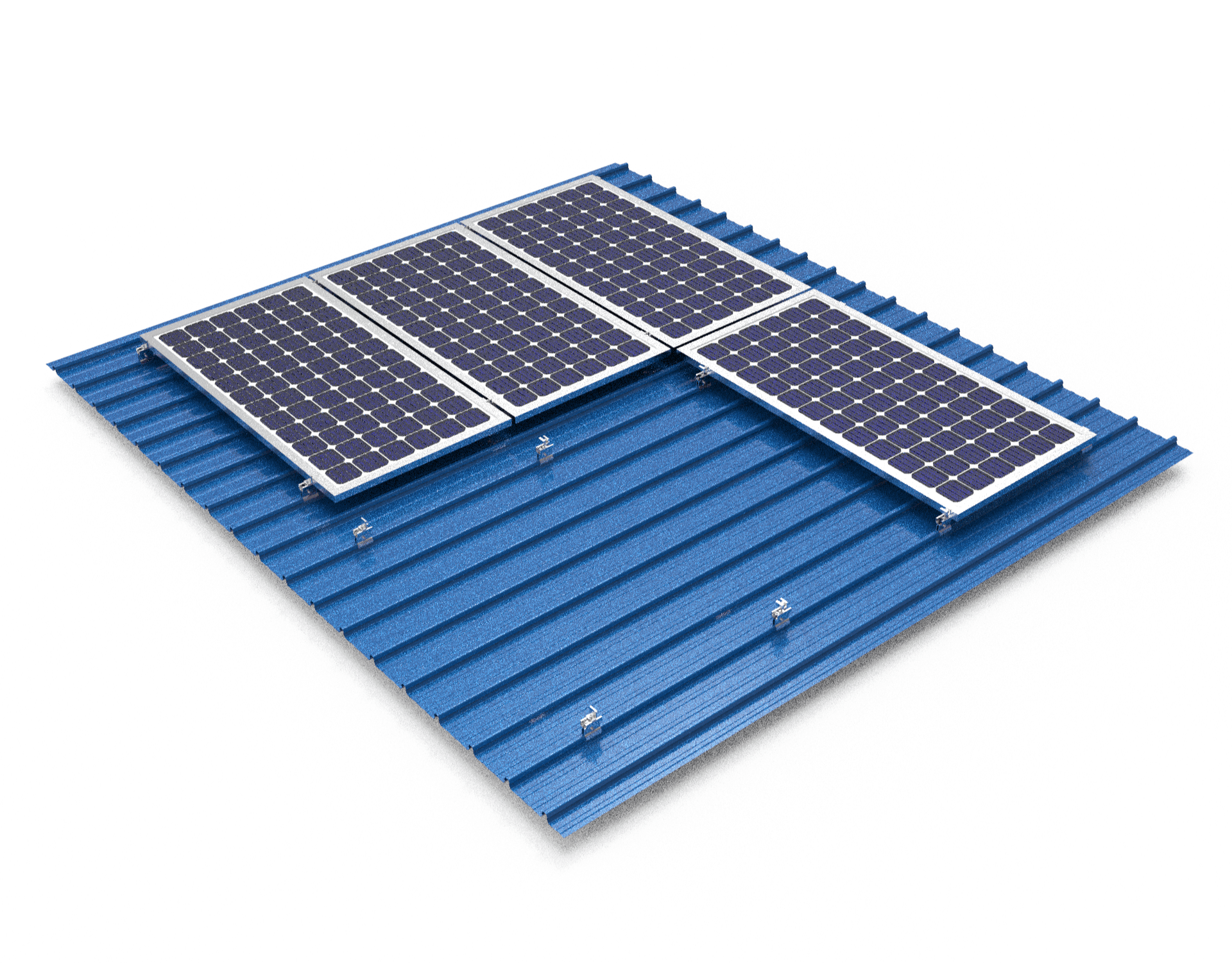
I. Introduction to Standing Seam Metal Roofs
A. Popularity and Benefits
Standing seam metal roofs (also known as seam roofs) have increased in popularity for pitched roofs, especially in the educational and leisure sector. Seam roofs are commonly made from steel, aluminium, and zinc. Key benefits include:
- Aesthetically pleasing look
- Robustness and weatherproof qualities
- Cooling effect from reflective coating, reducing energy use by up to 20%
These benefits complement solar PV mounting systems extremely well.
There are several major standing seam manufacturers, producing various seam types:
- Straight or round folds
- Single or double folded
| Seam Type | Description |
| Straight | Evenly spaced flat seams |
| Round | Curved seams |
| Single | One fold |
| Double | Two folds |
The seams are secured to the purlins using clips, allowing the panels to move freely as temperature changes. Solar mounting systems use clamps attached directly over the seams without penetrating the roof membrane.
B. Types and Manufacturer
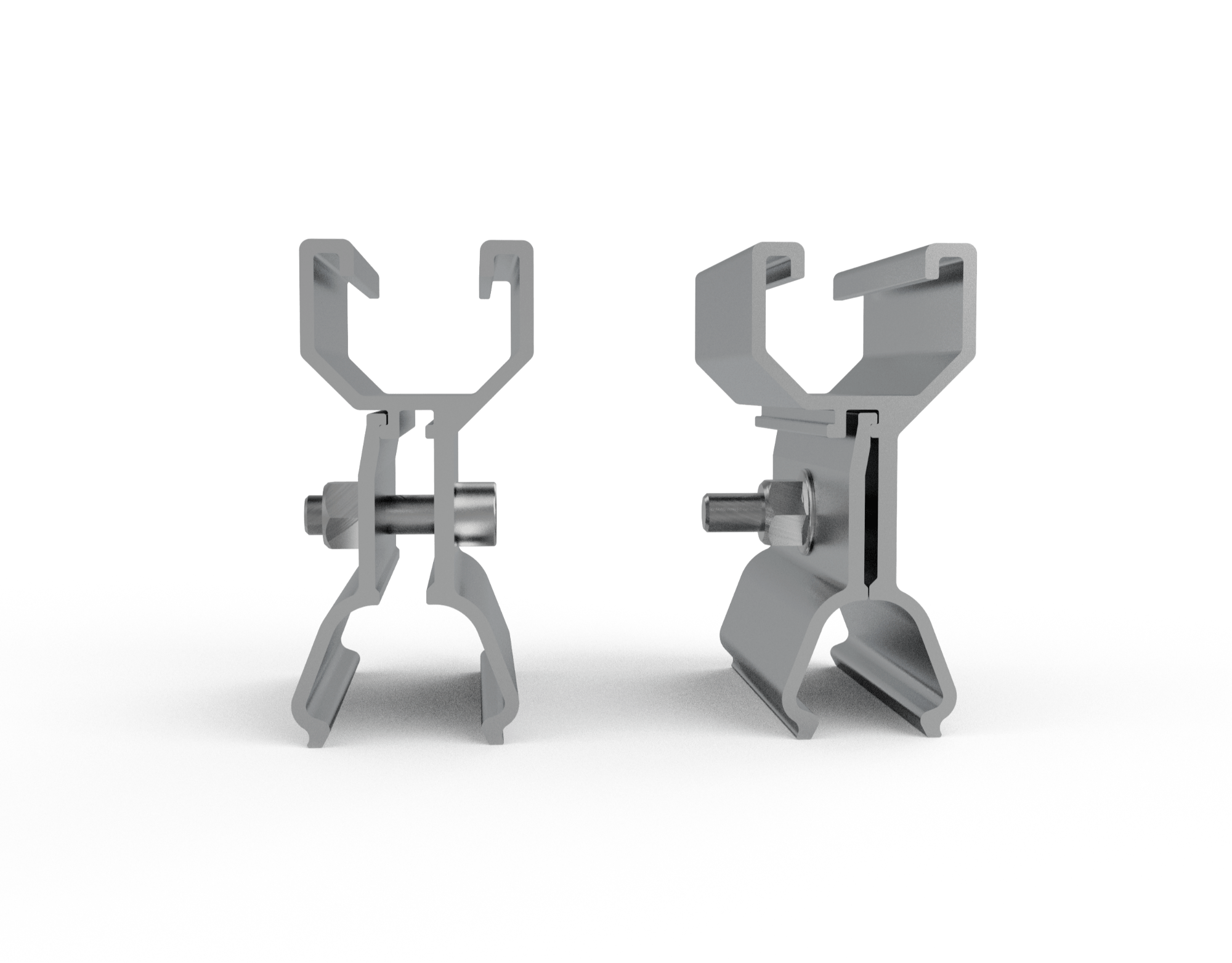
Common standing seam materials:
- Steel (painted/unpainted, galvanized, Galvalume)
- Aluminum
- Zinc
- Copper (rarely)
Major seam roof manufacturers:
- Kalzip
- Zinc
- Domitec
- GBS
- Klip-Lok
There are many profiles and dimensional variances. It’s important to match the manufacturer and panel details to the appropriate seam clamp system.
II. Mounting Methods
There are two main methods to mount solar PV systems onto standing seam metal roofs:
A. Seam Clamps:
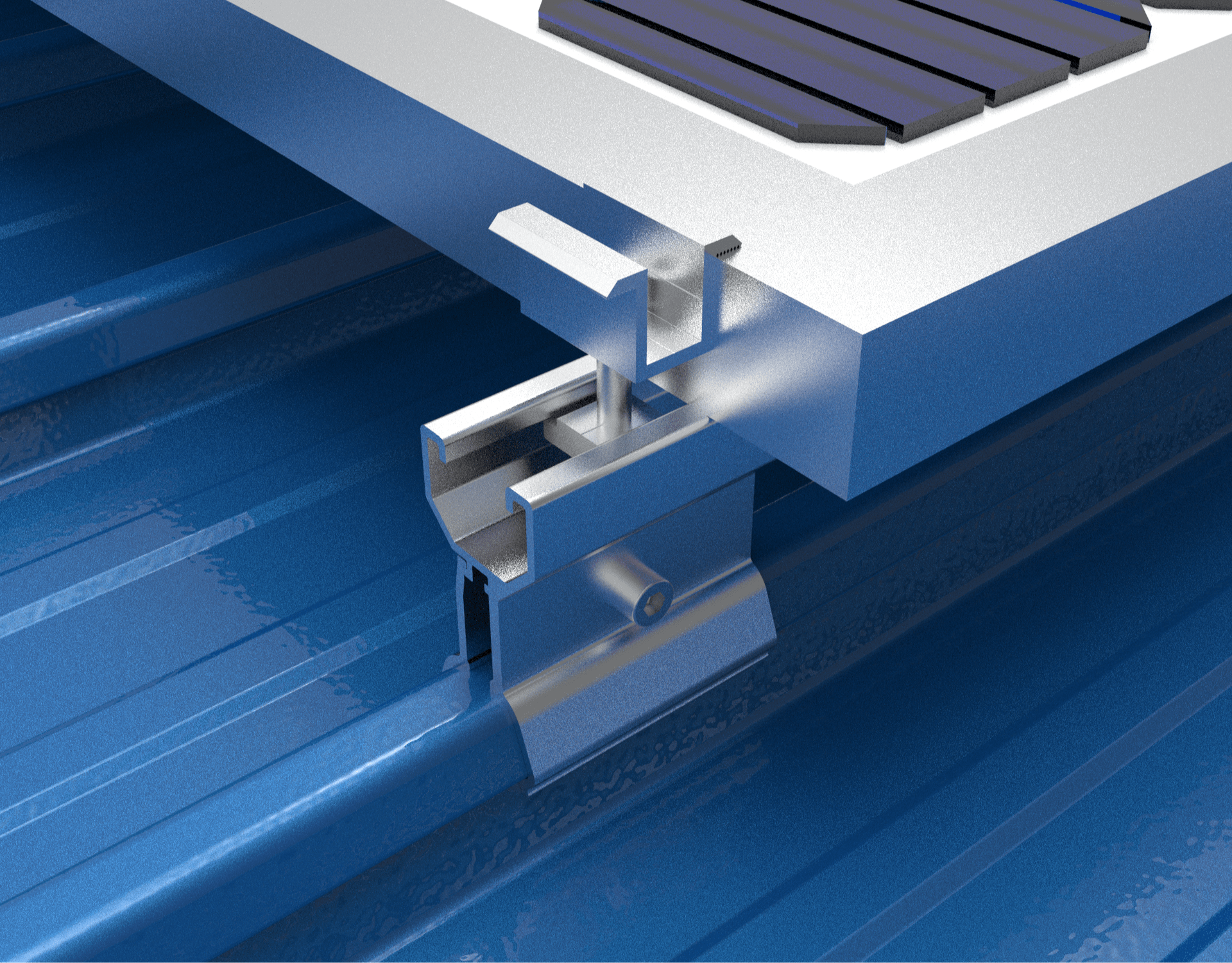
Attachment hardware (rails/direct mounting)
Seam clamps
Seam clamps secure onto the raised seams mechanically, without penetrating the roof membrane. This avoids risk of leaks.
1. Securing Method:
The clamps pinch the seam using round point set screws to create a strong mechanical interlock. The clamps grab onto the full beam-like structure of the seam.
2. Location Considerations:
- Avoid mounting over panel clips allowing expansion/contraction
- Follow manufacturer guidance on seam clamp placement
- Spread clamps evenly based on load calculations
| Clamp Type | Description |
| End clamps | Anchor start/end of row |
| Mid clamps | Secure middle of panels |
| Specialty clamps | For corners or transitions |
B. Attachment Hardware:
1. Rails:
Aluminium rails bolt onto the seam clamps, spanning multiple seams. Modules mount to rails. More parts but better space utilization.
2. Direct Mounting:
Module clamps attach directly to seam clamps without rails. Fewer parts, lower cost and weight. But less adjustment flexibility.
For proper structural integrity:
- Use tested, high-quality components.
- Follow manufacturer specifications.
- Consult a structural engineer.
III. Key Considerations
There are several important factors to consider when installing solar PV systems onto standing seam metal roofs.
A. Roof Warranty and Regulations:
- Verify with the roof manufacturer that seam clamps will not void warranties
- Some manufacturers specify their own clamps to use
- Follow all local building codes and solar regulations
B. Seam Compatibility:
- The clamp must match the exact seam profile and dimensions
- Select gauges tested with specific panel profiles and materials
- Avoid mismatching metals (e.g. copper)
C. Strength Testing:
- Use published strength ratings from accredited labs
- Account for SSMR material, gauge, coating, and profile
- Recognize tests exceed panel/building strength limits
| Strength Considerations | Description |
| Clamp-to-seam | Ultimate interlock strength |
| Panel flexural | Panel bending capacity |
| Roof attachment | Pull-out resistance |
| Buckling | Roof beam buckling mode |
D. Attachment Frequency:
- Clamp strength ≠ entire system strength
- Spread attachments based on load analysis
- Avoid concentrated loading through beams
E. Costs
| System | Cost per Watt |
| Large | As Per Watt |
| Small | As Per Watt |
Consider rails vs direct mounting. Evaluate parts, shipping, labour.
IV. Additional Resources
There are industry associations and manufacturer guides available with further guidance on solar mounting best practices for standing seam metal roofs.
1. Industry Guidelines:
Metal Construction Association – Technical bulletins on:
- Seam clamp compatibility
- Fastener usage with metal panels
- Metallurgy of aluminium, galvanized steel, etc.
Solar Energy Industries Association – PV system siting and mounting considerations
2. Manufacturer Information:
A. Roofing Manufacturers:
- Review warranty info regarding attachments
- Follow manufacturer mounting guidelines
- Utilize approved clamps
B. Clamp Manufacturers:
- Published strength test results
- Seam measurements and matched clamps
- Design recommendations
C. Mounting Hardware Manufacturers:
- Follow specifications on components
- Design guidance and engineering support
| Resource Type | What They Provide |
| Roofing | Warranty info, mounting guidelines, approved clamps |
| Clamps | Test results, seam details, design guidance |
| Mounting | Specifications, engineering support |
D. Qualified Professionals:
Consult qualified solar integrators, roofers, and structural engineers trained in saddle seam roofing. Get project-specific advice accounting for all variables.
Leverage multiple resources to ensure attachments preserve roof integrity and system longevity.
V. Conclusion
In summary, standing seam metal roofs provide an ideal mounting surface for solar PV systems when proper methods are used.
A. Summary of Advantages:
Key benefits of pairing seam roofs and PV:
- Aesthetic appeal
- Enhanced energy efficiency
- Convenient structural attachment points
- Non-penetrating seam clamps avoid leaks
- Long-term durability using quality components
By following best practices for design and installation, you can achieve an integrated, high-performing system.
B. Role of Professionals:
Work with qualified experts in:
- Solar integration
- Structural engineering
- Metal roofing and attachments
Experts should:
- Accurately assess needs
- Guide appropriate mounting method selections
- Conduct project-specific calculations
- Oversee safe, high-quality execution
This ensures roof integrity, system longevity, and code compliance.
C. Ongoing Developments:
As technology improves, expect advancements in:
- Efficient panel and inverter components
- Cost-effective rail less mounting
- Robust attachment clamps
- Streamlined design tools
Stay up-to-date on innovations allowing faster, lower-cost PV mounting on seam roofs with maximum ROI.
Adhering to best practices, leveraging professional expertise, and utilizing cutting-edge mounting technology facilitates optimal solar installations on these ideal metal roofing surfaces.
Advantages of Steel Structures in Solar Mounting by Structura Metal in Aurangabad

Introduction:
In the quest for sustainable energy solutions, solar power has emerged as a frontrunner. An often underestimated aspect of solar installations is the choice of mounting structures. Structura Metal, a pioneering company based in Aurangabad, recognizes the immense potential of steel structures in solar mounting. This article uncovers the advantages of employing steel structures for solar mounting and how they significantly contribute to stability and durability.
Benefits of Steel Structures in Solar Mounting:
1. Enhanced Stability:
Steel structures bring an unmatched level of stability to solar mounting. Their robustness and load-bearing capacity ensure that solar panels remain securely in place even in challenging weather conditions, reducing the risk of damage and enhancing long-term performance.
2. Durability Beyond Compare:
When it comes to longevity, steel reigns supreme. Its resilience against environmental factors such as corrosion, UV radiation, and temperature variations ensures that your solar installation maintains its structural integrity over time.
3. Customizable Design Options:
Steel’s flexibility allows for intricate and tailored designs. Whether you require ground-mounted solar systems or integrated rooftop installations, steel solar racking systems can be customized to fit the unique specifications of your project.
4. Corrosion Resistance:
Structura Metal employs advanced corrosion-resistant coatings on its steel structures. This protection safeguards against rust and deterioration, extending the lifespan of the mounting system and ensuring consistent performance.
5. Sustainability in Action:
Choosing steel structures aligns with sustainability goals. Steel is recyclable, reducing the environmental impact of your solar project. Its durability also means fewer replacements, contributing to a greener energy solution in the long run.
6. Versatility in Applications:
From ground-mounted solar systems to rooftop installations, steel’s versatility accommodates various applications. Whether you’re considering commercial, industrial, or residential projects, steel solar mounts offer adaptability.
Steel vs. Aluminum Solar Mounts:
Steel structures offer numerous advantages over aluminum counterparts:
Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity: Steel’s exceptional strength ensures stability in high-stress conditions, outperforming aluminum in load-bearing capacity.
Longevity: The durability of steel makes it a cost-effective choice in the long run due to reduced maintenance and replacements.
Corrosion Resistance: Properly coated steel is more resilient against corrosion compared to aluminum.
Customization: Steel’s malleability allows for intricate designs that cater to specific project requirements.
Environmental Impact: Recyclable steel is a sustainable choice compared to aluminum.
Conclusion:
Structura Metal’s emphasis on steel structures for solar mounting presents an array of advantages. The enhanced stability, durability, and customization options that steel brings to solar panel installations are truly remarkable. As global energy demands evolve and sustainability takes center stage, opting for steel mounting solutions proves to be a smart choice. With its corrosion resistance, load-bearing capacity, and versatile applications, steel structures from Structura Metal pave the way for a stable and enduring solar future.
Structural Analysis for Solar Mounting Structures: Ensuring Safety and Stability
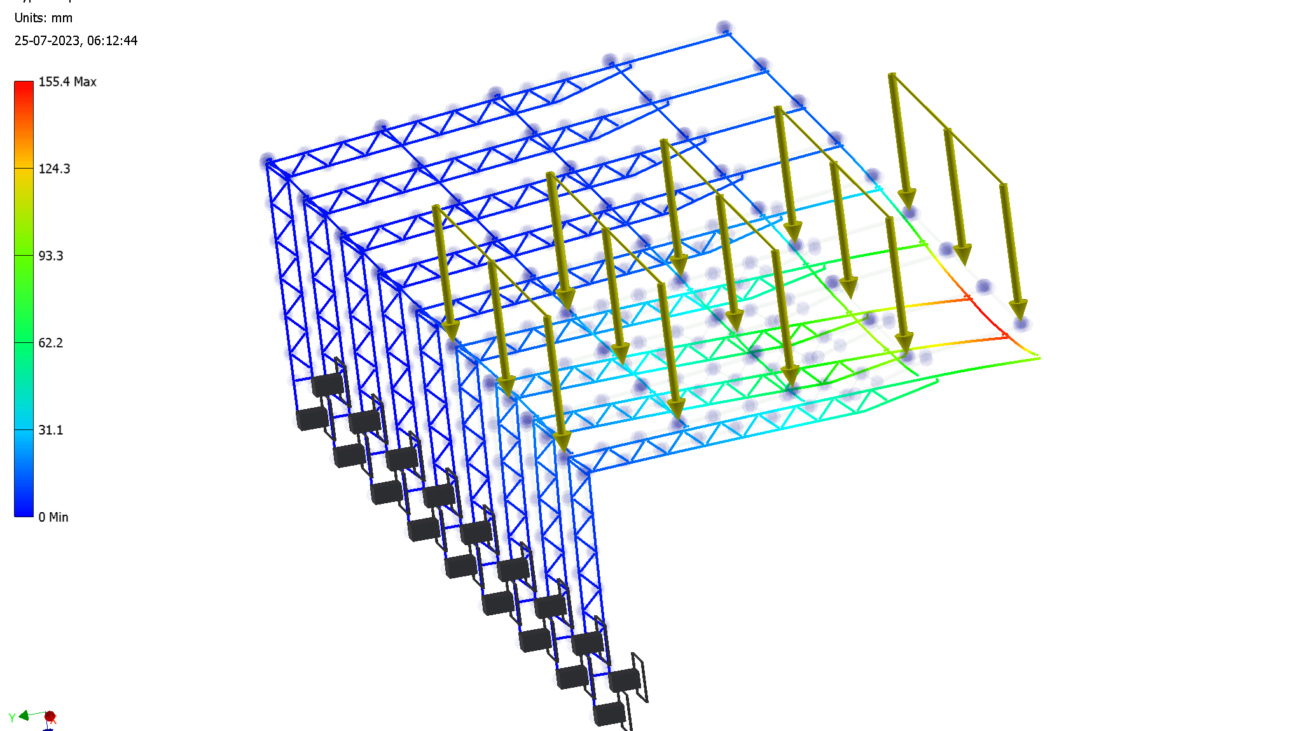
Solar mounting structures are the foundation of any solar power plant, and as such, their design, manufacturing, and installation must be done with the utmost care and attention to detail. One of the most critical elements of solar mounting structure design is structural analysis. This process involves analyzing the proposed structure to ensure that it can withstand the loads and forces it will be subjected to throughout its lifetime. In this blog, we will explore the importance of structural analysis for solar mounting structures and how it helps ensure safety and stability.
Why is structural analysis important for solar mounting structures?
Solar mounting structures are exposed to a variety of loads and forces, including wind, snow, and seismic activity. These loads and forces can cause the structure to deform, crack, or even collapse if the structure is not designed and manufactured to withstand them. Structural analysis is a critical step in the design process that helps to ensure that the proposed structure will be able to withstand these loads and forces without failure.
What are the different types of structural analysis?
There are several different types of structural analysis that can be used to evaluate solar mounting structures, including linear and nonlinear analysis, static and dynamic analysis, and linear and nonlinear buckling analysis.
Linear and nonlinear analysis: Linear analysis assumes that the structure’s behavior is linear and predictable, while nonlinear analysis takes into account the nonlinear behavior of the structure, such as buckling and plastic behavior.
Static and dynamic analysis: Static analysis assumes that the structure is in a state of equilibrium, while dynamic analysis takes into account the effect of time-varying loads and forces.
Linear and nonlinear buckling analysis: Linear buckling analysis assumes that the structure will buckle in a predictable and linear manner, while nonlinear buckling analysis takes into account the nonlinear behavior of the structure during buckling.
Which type of structural analysis is best for solar mounting structures?
The type of structural analysis that is best for a solar mounting structure will depend on the specific loads and forces that the structure will be subjected to. For example, if the structure will be exposed to high winds, dynamic analysis may be required. Similarly, if the structure will be located in an area prone to earthquakes, a seismic analysis may be necessary. It is important to consult with a structural engineer to determine the appropriate type of structural analysis for your solar mounting structure.
How is structural analysis conducted?
Structural analysis is typically conducted using computer-aided design (CAD) software. The designer will input the loads and forces that the structure will be subjected to into the software, and the software will then calculate the behavior of the structure under these loads and forces. The software will also generate detailed reports and drawings that the designer can use to evaluate the strength and stability of the structure.
In Conclusion,
Structural analysis is a critical step in the design and manufacturing of solar mounting structures. It helps to ensure that the structure will be able to withstand the loads and forces it will be subjected to throughout its lifetime, and that it will be safe and stable for the life of the solar power plant. By working with a structural engineer, solar power plant designers and manufacturers can ensure that their structures are designed and manufactured to the highest standards of safety and stability.
Introduction to Solar Mounting Structures
Solar Mounting Structures, also known as solar racking systems, are an essential component of any solar energy system. They provide the support and stability necessary for solar panels to function effectively and efficiently. In this report, we will provide an introduction to the basics of solar mounting structures, including the different types of systems available, the materials used to construct them, and the key considerations when designing and installing a solar mounting structure.
Types of Solar Mounting Structures
There are several different types of solar mounting structures available, each with their own unique features and benefits. The most common types include:
- Ground-Mounted Systems: These systems are installed directly on the ground and are typically used for large-scale solar projects, such as utility-scale solar farms. Ground-mounted systems are highly customizable and can be designed to meet specific site requirements.
- Roof-Mounted Systems: These systems are installed directly on the roof of a building and are commonly used for residential and commercial solar projects. Roof-mounted systems are available in a variety of styles, including flush-mounted, ballasted, and penetrating systems.
- Floating-Mount Systems: As their name suggests, these mounts are designed to float on water, making them ideal for installations on lakes and other bodies of water. Floating mounts are typically constructed of plastic or polymer, and they are designed to securely hold the solar array in place while also allowing for a certain amount of flexibility.
Materials Used in Solar Mounting Structures
The materials used to construct solar mounting structures are typically aluminum, steel, or a combination of both. Aluminum is a popular choice due to its lightweight, corrosion-resistant properties. Steel is also commonly used, particularly for ground-mounted systems, due to its strength and durability. Both materials can be coated with a variety of finishes to protect against weathering and corrosion.
Key Considerations When Designing and Installing a Solar Mounting Structure
When designing and installing a solar mounting structure, there are several key considerations that must be taken into account. These include:
- Site conditions: The solar mounting structure must be designed to withstand the specific site conditions, such as wind, snow, and seismic activity.
- Load capacity: The solar mounting structure must be able to support the weight of the solar panels and any additional equipment, such as inverters and batteries.
- Orientation and tilt: The solar mounting structure must be oriented and tilted to optimize solar panel performance and maximize energy production.
- Accessibility: The solar mounting structure must be designed to allow for easy access for maintenance and repairs.
In conclusion, solar mounting structures are an essential component of any solar energy system, providing the support and stability necessary for solar panels to function effectively and efficiently. Understanding the different types of systems available, the materials used to construct them, and the key considerations when designing and installing a solar mounting structure is important for ensuring the success of any solar project.
Types of coating used on solar mounting structures
Solar energy is a rapidly growing industry, and the durability and longevity of solar mounting structures are crucial for the efficient functioning of solar power systems. One of the key factors that determine the longevity of solar mounting structures is the type of coating used on them. In this blog post, we will discuss the different types of coatings used on solar mounting structures, their unique properties and the industry standard grading in use.
Anodized coating: Anodizing is an electrochemical process that creates a protective oxide layer on the surface of aluminium. This coating is highly durable, resistant to weathering, and provides excellent insulation. Anodized coatings are often used on aluminium solar mounting structures. AA10 is the common industry standard of anodized coating which is 10 microns thick.
Powder coating: This type of coating is applied as a dry powder and then cured under heat. It is an environmentally friendly process and provides a durable, long-lasting finish. Powder coating is often used for steel and aluminium solar mounting structures.
Galvanized coating: This type of coating is used to protect steel from corrosion. Galvanized coatings are available in two forms: electro-galvanized and hot-dip galvanized. Electro-galvanized coating is applied by electroplating zinc onto the steel, while hot-dip galvanized coating is applied by immersing the steel in a bath of molten zinc. Both types of galvanized coatings provide excellent corrosion resistance. Hot rolled sheets with Hot Dip Galvanizing coat ranging from 80 microns to special coating of 120 microns is the industry standard for hot-dip galvanized coating.
Galvalume coating: This type of coating is a type of alloy coating that is composed of a mixture of aluminium, zinc, and silicon. Galvalume coating is highly corrosion-resistant and provides excellent protection for steel solar mounting structures. 150 AZ coating is the industry standard for Galvalume coating.
PosMAC coating: POSMAC coating is a corrosion-resistant product that is 5 to 10 times stronger resistance than that of a normal hot-dip galvanized steel sheet [GI, GI(H)]with the same coating weight. PosMAC has an excellent cross-section corrosion resistance; normal thick plating products can be replaced with this product. The same processing, assembly, and painting process can be applied to PosMAC as one would apply to GI. GP Sheets with coating upto 550 GSM is the industry standard for PosMAC coating.
In conclusion, the type of coating used on solar mounting structures plays a crucial role in determining the longevity and durability of the structures. The use of anodized, powder, galvanized, Galvalume and PosMAC coatings provides excellent protection against corrosion and weathering, ensuring the efficient functioning of solar power systems. It’s important to choose the right coating based on the specific needs and requirements of the project.